Pressure = Force / Area
A pressure sensor is a device that measures the pressure of a gas or liquid and converts the measured value into an electrical signal as an output.Pressure sensors are used in everything from roads, to machinery, to vehicles, to weaponry, to laboratories.Types of pressure sensorPressure sensors can also be used to indirectly measure flow, speed, water level, and altitude
Basic Terminology
• Pressure Sensor - Device that produces a signal proportional to the change in pressure• Pressure Transducer or Pressure Transmitter- Pressure Sensors that have electronics to process signals and provide an amplified output
• Gage - Pressure measured relative to ambient pressure
• Absolute - Pressure measured relative to the vacuum of space
• Differential - The pressure difference between two separate pressures
• Line pressure - The ambient pressure that is applied to both sides of a differential sensor
• Full Scale - The difference between the maximum pressure and zero pressure
• Accuracy - The maximum deviation from a Best Fit Straight Line
• Drift - Gradual output change from calibrated state over time
• Resolution - The smallest difference between an output that can be meaningfully distinguished
• Over Pressure - The maximum pressure that can be applied without damaging the sensor
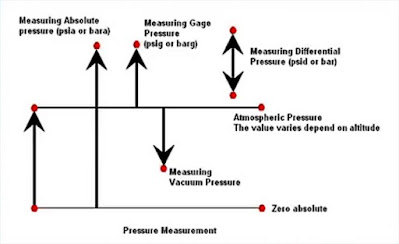
Gage, Differential, Absolute, and Vacuum Pressures
Gage Pressure Sensors - Pressure is made in a positive direction when compared to ambient pressure (14.69 psia,101.3 kPa, 1 Atm)
Absolute Pressure Sensor - Pressure are made relative to zero pressure (0 psia) in a positive direction
Differential Pressure Sensor - Measures the difference between one pressure (P1) to another pressure (P2)
(P1)110 psi - (P2)100 psi = 10 psid (∆P)
Vacuum Pressure Sensor - Pressure is are made relative to any set pressure in a negative direction
Best Fit Straight Line Types of pressure sensor
1. Multiple points of pressure are taken and the output is recorded
2. A best fit straight line (BFSL) is drawn to best represent the data
3. The points are measured for their deviation from the BFSL
4. The level of deviation allowed is the accuracy of the unit
Pressure Sensor Technologies
- Potentiometric Pressure Sensors
- Inductive Pressure Sensors
- Capacitive Pressure Sensors
- Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors
- Strain Gauge Pressure Sensors
- Variable Reluctance Pressure Sensors
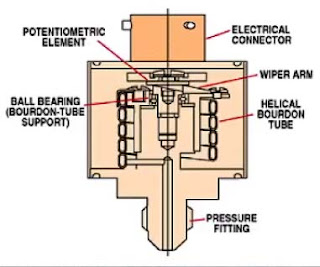
Potentiometric Pressure Sensors
• Uses a Bourdon tube, capsule, or bellows to drive a wiper arm on a
resistive element
Advantage
- Relatively inexpensive sensors used for coarse measurements
Disadvantage
- Repeatability and Hysteresis Errors
- Low Performance
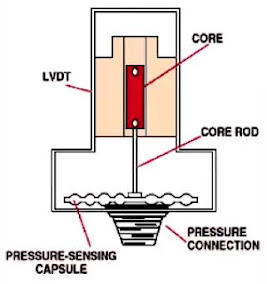
Inductive Pressure Sensors
Uses the LVDT of a moving core to vary the inductive coupling between
the transformer primary and secondary.
Advantage -
- Withstand harsh environmental condition
- Longer Life
Disadvantages -
- Very Low Frequency Response
- Require filtering if a DC output is desired
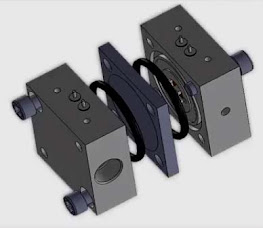
Capacitive Pressure Sensors
Applied pressure causes the diaphragm to deflect and the capacitance
to change
C =µ A/d
Advantages
- Accuracy
- Durability
Disadvantages
- Sensitive to Temperature and Capacitance
- Low Frequency Response
- Large
Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors
Bi-directional transducers capable of converting stress into an electric potential and vice versa Consist of metallized quartz or ceramic materials
Advantages -
- Small
- High Frequency Response
- Low Displacement
Disadvantages
- Long Term Stability
- Sensitive to Temperature
Strain Gauge Pressure Sensor
When silicon is deformed by applied stress, the resistance changes. This
is called the piezoresistive effect
RO = rhoL/WT
Advantages
- Fast Response Time
- Temperature Compensation
- Accuracy
Disadvantages
- Unable to provide lower ranges
- Low level outputs
- Long Term Drift
Variable Reluctant Pressure Sensor
A magnetic circuit is formed and a pressure causes a mechanical
defection of a diaphragm
Advantages
- Can be used to measure gasses as well as liquids.
- Rugged and reliable under high stress
- Withstand extreme temperatures and harsh media
- High output at all pressures
Disadvantages
- Relatively larger size
- Needs signal amplification






Post a Comment